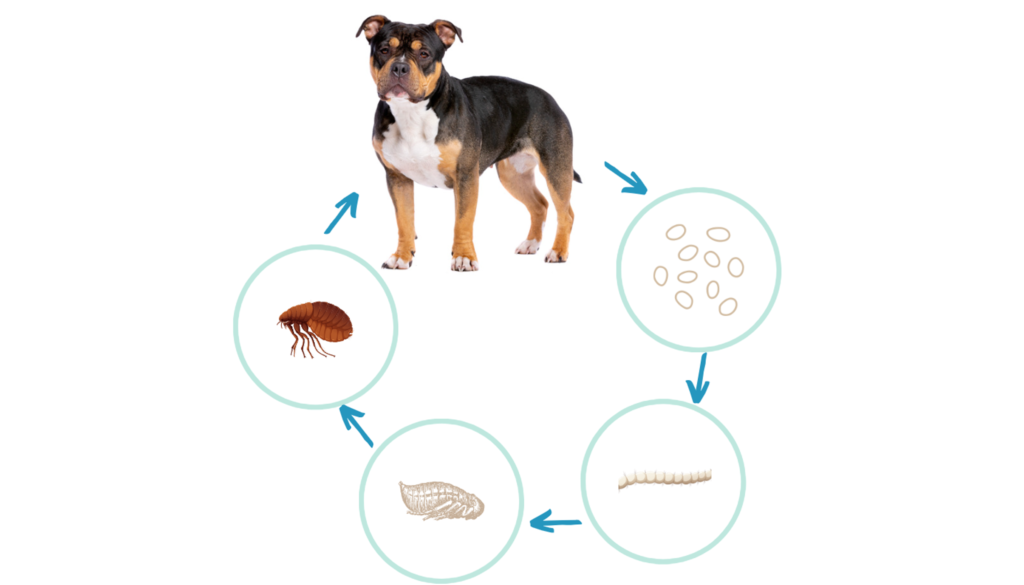
The Life Cycle of Fleas
The life cycle of fleas typically consists of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
Here’s a brief overview:
Egg: Female fleas lay eggs on their host animal (your dog) or in the environment (such as carpets, bedding, or soil). Flea eggs are tiny, oval-shaped, and white, and they usually hatch within 2-12 days, depending on environmental conditions like temperature and humidity.
Eggs can fall off your dog and continue their life cycle. Flea eggs are quite resilient and can survive a wide range of temperatures. However, they are more likely to hatch and develop in warmer environments with temperatures ranging from 70°F to 85°F (21°C to 29°C) and high humidity levels. Extreme temperatures, such as freezing temperatures, can kill flea eggs, but they are generally more resistant to cold than other stages of the flea life cycle. Additionally, flea eggs may also be destroyed by high temperatures above 95°F (35°C).
Larva: Once the eggs hatch, they release larvae. Flea larvae are small, worm-like creatures with a whitish color and no legs. They feed on organic matter, such as flea feces, dead skin cells, and other debris found in their environment. Flea larvae undergo several molts as they grow, typically over a period of 5-14 days.
Pupa: After the larval stage, flea larvae spin silken cocoons and enter the pupal stage. Inside the cocoon, they undergo metamorphosis, transitioning into adult fleas. The pupal stage can last anywhere from several days to several months, depending on environmental conditions. Fleas in the pupal stage are resistant to environmental stressors and difficult to detect.
Adult: Once development is complete, adult fleas emerge from their cocoons. They are small, wingless insects with flattened bodies, designed for moving efficiently through fur. Adult fleas must feed on blood within a few days to survive and reproduce. Female fleas can lay hundreds of eggs over their lifespan, perpetuating the flea life cycle.
It’s important to note that environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and the availability of hosts can influence the duration of each stage of the flea life cycle. Understanding the flea life cycle is crucial for effective flea control and prevention measures. To learn how to get rid of fleas naturally, here’s an article to help.